Problem: Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a "linked list":
- The "linked list" should use the same TreeNode class where the right child pointer points to the next node in the list and the left child pointer is always null.
- The "linked list" should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example:
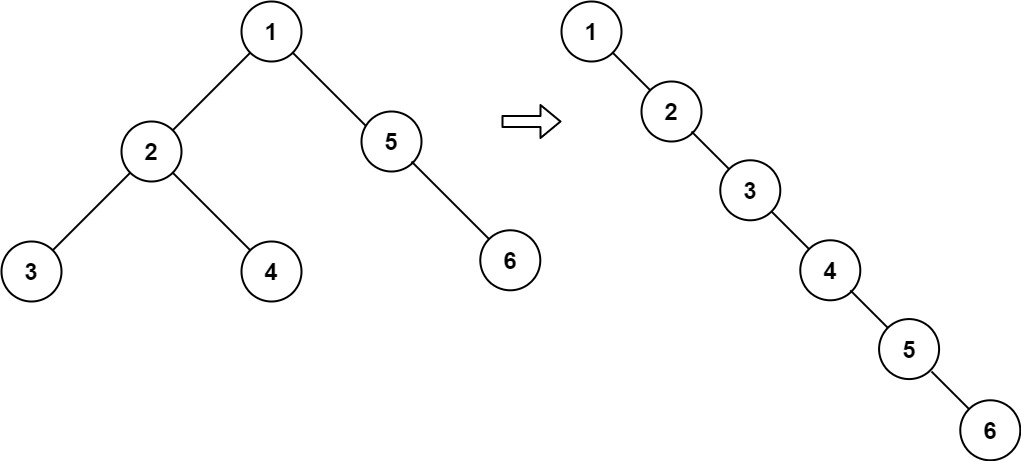
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Input: root = [] Output: []
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Approach: We can use kind of reverse postorder traversal and while using that we can maintain a prev node.
Implementation in C#:
public void Flatten(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
TreeNode prev = null;
this.FlattenUtil(root, ref prev);
}
private void FlattenUtil(TreeNode node, ref TreeNode prev)
{
if (node == null)
{
return;
}
this.FlattenUtil(node.right, ref prev);
this.FlattenUtil(node.left, ref prev);
node.right = prev;
node.left = null;
prev = node;
}
Complexity: O(n)
No comments:
Post a Comment